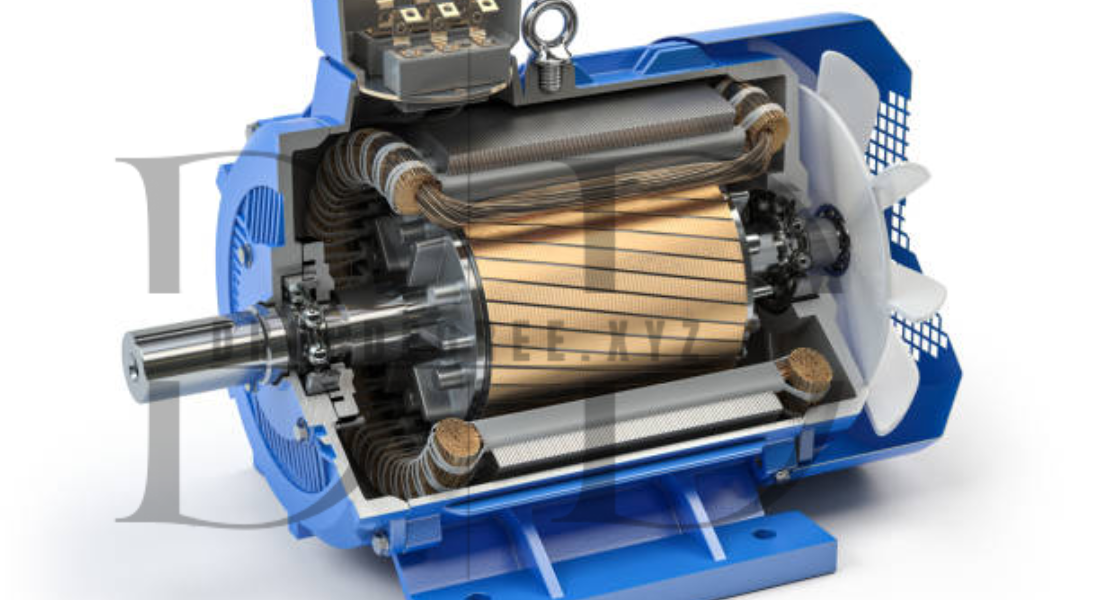
Electric motors are fundamental to modern life, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machines. They consist of several critical components, each playing a vital role in ensuring efficient performance. Understanding the function and significance of electric motor components can help in maintaining, troubleshooting, or designing more energy-efficient systems. In this article, we’ll break down the key parts of an electric motor and their functions, providing you with a comprehensive guide to these essential devices.
What Are Electric Motors?
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is widely used in various applications such as fans, pumps, electric vehicles (EVs), and industrial equipment. The motor operates on the principle of electromagnetism, where current passing through a coil generates a magnetic field that interacts with permanent magnets, creating motion. The efficiency, speed, and torque produced by the motor depend on the various electric motor components.
Key Electric Motor Components
Understanding electric motor components is crucial for both users and manufacturers. Below are the primary parts that make up an electric motor.
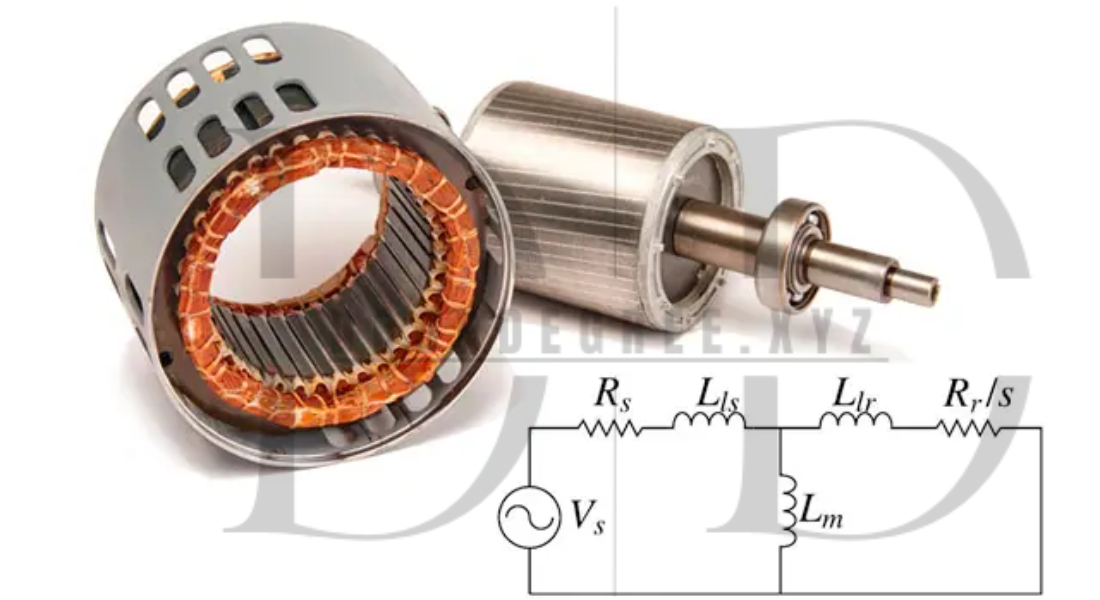
1. Stator
The stator is the stationary part of the motor and plays a pivotal role in generating the magnetic field. It consists of a set of coils or windings wound around a laminated core. When an electric current flows through these windings, it creates a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the rotor, generating motion.
- Function: The stator generates the magnetic field needed to power the rotor.
- Importance: It influences the motor’s efficiency, speed, and power output.
2. Rotor
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, usually located inside the stator. It is typically made of copper or aluminum and is attached to the shaft of the motor. The rotor’s role is to rotate as a result of the magnetic field created by the stator.
- Function: It converts the electromagnetic force from the stator into mechanical energy.
- Importance: The rotor’s design impacts the efficiency and torque of the motor.
3. Commutator (for DC Motors)
In DC motors, the commutator is a critical component that helps in reversing the direction of current flow through the rotor windings. This reversal ensures that the rotor continues to spin in the same direction. It is a split ring made of copper segments that come in contact with the brushes.
- Function: To reverse current direction and maintain rotor motion.
- Importance: It allows the motor to operate efficiently and continuously.
4. Brushes (for DC Motors)
Brushes are small carbon or graphite blocks that maintain electrical contact with the commutator. They allow current to flow from the external power source into the rotor windings, enabling the motor to operate.
- Function: To conduct electricity to the rotor.
- Importance: Brushes wear out over time and need regular maintenance.
5. Shaft
The shaft is a mechanical component that connects the rotor to the external mechanical system, such as a fan blade or conveyor belt. It transmits the rotational energy generated by the rotor to the output device.
- Function: To transmit mechanical energy from the rotor to the load.
- Importance: A robust shaft is critical for transferring energy efficiently without damage.
6. Bearings
Bearings are used to support the shaft and allow it to rotate smoothly within the motor casing. They reduce friction and wear, ensuring that the motor operates quietly and efficiently.
- Function: To minimize friction and support the rotor’s movement.
- Importance: High-quality bearings increase the motor’s lifespan and efficiency.
7. End Bells (or End Shields)
End bells are protective covers placed at both ends of the motor. They enclose the bearings and the rotor, providing structural support and preventing contaminants from entering the motor.
- Function: To protect the internal components and support the bearings.
- Importance: They ensure the motor remains protected from dust, dirt, and moisture.
8. Cooling System
Electric motors generate heat during operation. A cooling system, such as a fan or liquid cooling mechanism, is often incorporated to maintain the motor’s optimal operating temperature.
- Function: To dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
- Importance: Cooling systems ensure the motor does not overheat, improving efficiency and prolonging lifespan.
9. Windings
Windings are coils of wire that form part of the stator and rotor. These wires are typically made of copper, as it is an excellent conductor of electricity. The windings play a key role in generating the electromagnetic field that drives the motor.
- Function: To carry electrical current and create a magnetic field.
- Importance: High-quality windings reduce energy losses and enhance motor performance.
Types of Electric Motors and Their Components
Electric motors come in various types, each with unique configurations of components based on their intended application. The two most common types are:
AC Motors (Alternating Current Motors)
AC motors are widely used in industrial and residential applications. These motors use an alternating current to power the stator, which generates the magnetic field. The rotor then rotates as it interacts with this magnetic field. AC motors do not require brushes or a commutator.
- Key Components: Stator, rotor, bearings, and cooling system.
- Common Applications: Fans, compressors, HVAC systems, and home appliances.
DC Motors (Direct Current Motors)
DC motors use a direct current to power the stator, and they incorporate a commutator and brushes to reverse the current direction. These motors are often used when variable speed control is necessary.
- Key Components: Stator, rotor, commutator, brushes, and bearings.
- Common Applications: Electric vehicles, robotics, and small appliances.
How Electric Motor Components Work Together
The success of an electric motor depends on how all of its components work in harmony. The stator creates a magnetic field, which induces a force on the rotor, causing it to rotate. The rotor, in turn, powers the connected mechanical system through the shaft. Bearings ensure smooth rotation, while the cooling system prevents the motor from overheating.
In a DC motor, the commutator and brushes work together to ensure continuous current flow, while in AC motors, the alternating current eliminates the need for these components. Regardless of the motor type, each component is crucial for efficient performance.
Maintenance and Care for Electric Motor Components
Proper maintenance of electric motor components is essential for ensuring longevity and peak performance. Regular inspection of key parts such as bearings, windings, and the cooling system can prevent costly repairs. Additionally, keeping the motor clean and free from debris can enhance its lifespan.
- Lubrication: Keep bearings properly lubricated to minimize friction.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the motor to remove dust and dirt.
- Inspections: Check the windings for damage and test the motor’s performance regularly.
Conclusion
Electric motors are complex machines with various critical components, each contributing to the motor’s efficiency and performance. From the stator and rotor to the bearings and cooling systems, every part has a vital role in ensuring the motor works seamlessly. Whether you’re designing, maintaining, or troubleshooting an electric motor, understanding its components is essential for optimal performance. By regularly inspecting and maintaining these components, you can maximize the lifespan and efficiency of your motor.
By delving into the details of electric motor components, you gain a deeper appreciation of how these parts work together to produce reliable, efficient power for countless applications. Whether you’re in the industrial sector or simply rely on household appliances, the electric motor’s inner workings are what make many modern technologies possible.
